Planning your Talk Architecture
Talk is architected to be able to run on as little as 500MB of RAM. To do this however you will need to use the pre-compiled Docker container, as compiling the code and dependencies will cause a memory spike.
For the average small blog or newsroom, these are our recommended machines:
- Digital Ocean: ~$5/month for their 1GB droplet
- Google Cloud: ~$14/month for a g1 small
- AWS: ~$16/month for a t2small
From there, you’re free to separate app servers and DB servers, and scale up as much as you need.
One larger newsroom’s setup, as an example of Talk performing at scale, is:
Application servers: c4.xlarge (16 VM nginx + Talk VM machine pairs) Mongo nodes: 3x c3.medium (large db cluster, 1 master, 2 read replicas)
If you need help with Talk performance or want custom scaling help or recommendations, let us know by logging a ticket and one of our engineers will get in touch with you: https://support.coralproject.net
How to Scale Talk Components
Scaling the Talk Application
In addition to scaling by adding additional app servers, Talk as a server component can flex to various roles. Depending on the desired configuration the roles can be split up to ensure high availability, and best matching to underlying host resources.
There are three components to the Talk application that can be served independently or in combination on a single thread: API Server, WebSockets, and Jobs
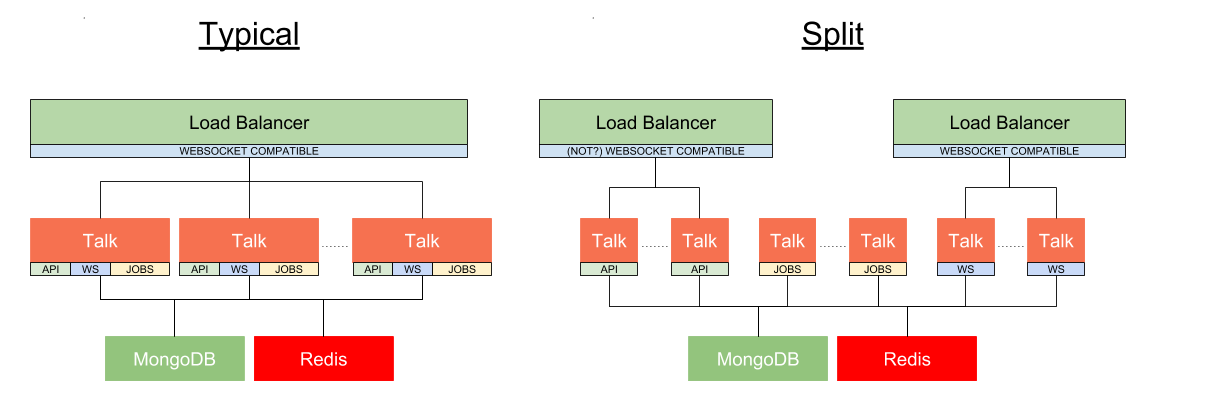
In the diagram we see the difference between a Typical configuration (which just adds additional Talk application instances) vs the Split configuration where different Talk components could be spread across different machine resources to optimize infrastructure utilization. See Serving the Application
Scaling Redis
Redis serves as a general cache and pub/sub broker. We treat all the data stored in Redis as ephemeral, so using as a cache serves us well for Talk to synchronize expensive query caches. It also serves as our pub/sub broker for use with live updates as propagated through the GraphQL subscription system. For this reason it is not recommended to implement multiple instances of Redis.
Scaling MongoDB
MongoDB is treated as our general store for persisted data. Talk supports the most common strategies for scaling MongoDB instances including replicas and/or sharding. Depending on your specific data use cases, refer to MongoDBs documentation for more information about scaling https://www.mongodb.com/mongodb-scale.
Load Balancer
While this subject lives outside the Talk ecosystem, it is critical for application delivery. For websockets to work correctly, a load balancer must be selected that can support long lived connections that are required for websockets to work.
Running Talk in Production
When you are ready to launch your production instance of Talk update your NODE_ENV environment variable from development to production mode.
Then launch talk with yarn start or with the command NODE_ENV=production ./bin/cli-serve -j -w
By default Talk will run on a single thread, but you can also run multiple Talk threads on a single application instance by setting the environment variable TALK_CONCURRENCY. See Advanced Configuration